How Does Gadovist® Work?
How Does Gadovist® Work?
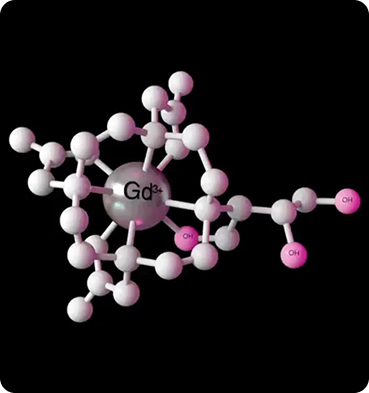
The active ingredient in Gadovist® is gadobutrol.
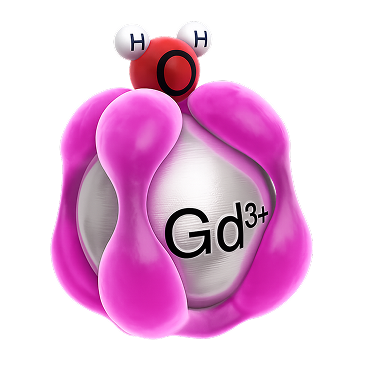
Gadobutrol contains gadolinium (Gd3+) which is firmly bound in a macrocyclic complex.
Gadolinium is a rare earth element, which causes contrast enhancement in MRI scans.

The mode of action is the same as with all currently marketed extracellular Gd-containing products.

A high concentration and high relaxivity of Gadovist® results in the highest T1 shortening per mL versus other marketed products, thus resulting in excellent image quality.1

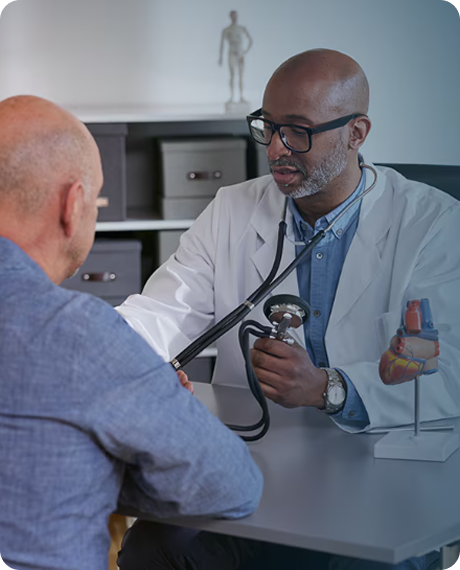
Safety Information
GADOVIST 1.0 (gadobutrol) is indicated in adults and children of all ages including term newborns for:
- Contrast enhancement during cranial and spinal MRI investigations and for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA).
- Contrast enhanced MRI of the breast to assess the presence and extent of malignant breast disease, and MRI of the kidney.
- GADOVIST 1.0 is particularly suited for cases where the exclusion or demonstration of additional pathology may influence the choice of therapy or patient management, for detection of very small lesions and for visualization of tumors that do not readily take up contrast media.
- GADOVIST 1.0 is also suited for perfusion studies for the diagnosis of stroke, detection of focal cerebral ischemia and tumor perfusion.
Consult the product monograph for important information about:
- The most serious warnings and precautions, which include the use of GBCAs and the risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) and the risks of off-label intrathecal use
- Other relevant warnings and precautions regarding gadolinium accumulation in the brain, use in patients with hypersensitivity reactions and use during pregnancy
- Conditions of clinical use, adverse reactions, drug interactions and dosing instructions
The Product Monograph is also available by calling Bayer Medical Information at 1-800-265-7382.
Spot Gadovist® Trivia
Can You Pick Out Gadovist®?


Benefits
A Good Investment in Patient Care
An investment in Gadovist® is a good investment in patient care. Gadovist® provides superior results compared to other Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs).
Benefits for you and your patient include:
 Less contrast agent used6-8
Less contrast agent used6-8 Increased signal and contrast on images3-9
Increased signal and contrast on images3-9 Enhanced image quality3
Enhanced image quality3 Higher sensitivity and accuracy for detection of malignancy4
Higher sensitivity and accuracy for detection of malignancy4 Improved diagnostic confidence4,5
Improved diagnostic confidence4,5
Using Gadovist® also means unlocking access to the radiology portfolio of solutions that Bayer Canada offers.
Learn More
Want to know more?
References:
* Relaxivity is a marker for the ability of a GBCA to enhance signal intensity on the magnetic resonance image and a prerequisite of technical efficacy of GBCAs.11 § Three independent blinded readers assessed off-site their overall diagnostic preference (primary efficacy parameter) based on a matched peers’ approach. ¶ Assessments in which a preference for either agent was expressed (p<0.001). No preference recorded in a further 175. † Other GBCAs include Dotarem® and ProHance®. ‡ At equal contrast dose
- Rohrer M, Bauer H, Mintorovitch J, et al. Invest Radiol. 2005;40(11):715–24.
- Szomolanyi Q, et al. Invest Radiol. 2019;54(9):559-564.
- Anzalone N, et al. Neurosurgery 2013;72(5):691–701.
- Gutierrez JE, et al. Magn Reson Insights 2015; 8:1–10.
- Katakami N, et al. Invest Radiol 2011;46(7):411–18.
- Gadovist® Product Monograph. April 2025.
- Dotarem® Product Monograph. April 2018.
- ProHance® Product Monograph. May 2022.
- Kanal E, Maravilla K and Rowley HA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2014;35(12):2215–26.
- Anzalone N, et al. Eur J Radiol 2013;82(1):139–45.
- Tóth É, Helm L and Merbach A. Second Edition ed: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2013:25–81.
- Maravilla KR, Smith MP, Vymazal J, et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36(1):14–23.
- Koenig M, Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Piontek M, et al. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(12):3287–3295.
- Maravilla KR, San-Juan D, Kim SJ, et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38(9):1681–1688.
- Saake M, Langner S, Schwenke C, et al. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(3):820–828.